You can find diamonds in every known color, including blue, green, brown and black.
Colored diamonds are known as fancy stones and are very rare. In fact, only 0.001
percent of all diamonds are colored stones.
Grading Color
The most common diamonds are colorless-white to yellow or brown stones. The color
is defined by the colors of the light rays that pass through the stone. These diamonds
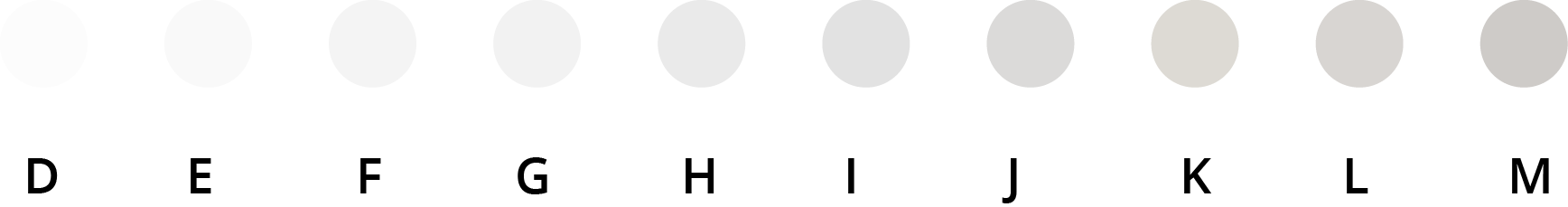
are graded on a scale from D to Z. The letter D represents absolutely colorless
diamonds. Any letter after D represents one grade lower from transparent. The final
letter, Z, refers to a yellow stone.
Fancy Colors
Rare and very expensive, colored or "fancy" diamonds are becoming ever more popular.
These diamonds reflect the colors of the rainbow and dazzle in brilliant combinations
of red, pink, blue, yellow, orange, green and brown.
Yellow is the most common colored diamond, while pink, red, blue and green diamonds
are extremely rare. Colored diamonds also tend to be smaller than other diamonds
and they are cut to maximize color, not clarity.
The appearance of the color is described with three elements:
- Hue - the predominant color.
- Tone - the darkness of the color.
- Saturation - the intensity of the color.
Colored diamonds are described based on their predominant hue, such as "pink." If
for example, the fancy diamond contains hints of a secondary color such as purple,
it will be described as "purplish pink." The use of "ish" indicates the subtle presence
of purple. However, a fancy diamond described "brown pink" means that the appearance
of both colors is virtually even throughout the stone.
The GIA uses specific grades to identify the ranges of color:
- Faint
- Very light
- Light
- Fancy Light
- Fancy
- Fancy Intense
- Fancy Vivid
For example, a fancy intense yellow may be listed as FIY or a fancy light pink as
a FLP. These grades play a significant role in determining the value of colored
diamonds; the stronger the hue the more valuable the diamond.
Various ways of "treating" a diamond, such as heat, can be used to intensify or
enhance the color. However, these treated stones are worth far less per carat than
their natural counterparts.